September 12, 2022
Bony Landmarks Of Chest
- Accurate and consistent radiographic positioning requires certain landmarks or reference points, that can be used to center the image receptors (IR) correctly to ensure that all essential anatomy is included on that specific projection.
- These landmarks should be parts of the body that can easily be located in patients, such as part of the bony thorax
- For chest positioning, the landmarks are:-
- Vertebral Prominent ( Seventh Cervical Vertebra):-
- The vertebral prominence is an important landmark for determining the central ray (CR) location on a posteroanterior (PA) chest projection.
- It is the spinous process of the 7th cervical vertebrae.
- It can be palpated readily on most patients by applying light pressure with the fingertips at the base of the neck.
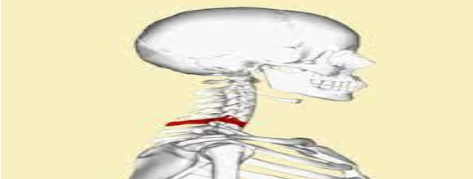
- Jugular Notch :-
- The suprasternal notch, also known as the fossa jugularis sternalis, or jugular notch.
- It is important for determining the CR placement anteroposterior (AP) chest projections.
- This is palpated easily as a deep notch or depression on the superior portion of the sternum
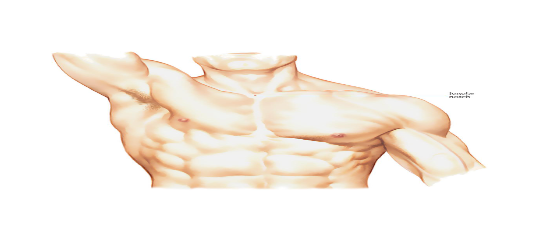
- Sternal Angle:-
- The sternal angle is formed at the articulation of the manubrium and the body of the sternum. It is also called the angle of Louis.

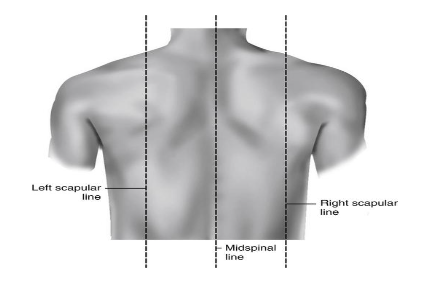
Mid Thorax:-
- It is a prominent landmark that is easily palatable at the mid sternum and posteriorly at the level of T7.
- It can be seen at the level of the inferior angle of the scapula.
- It is used in chest PA and AP.
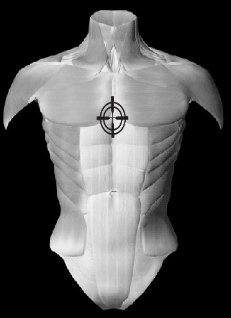
PA(Posterior – Anterior) VIEW
The Posteroanterior (PA) chest X ray examines the lungs, bony thoracic cavity, mediastinum, and great vessels.
Indication of this x-ray is
- Pneumonia- It is a condition in which air is filled in alveoli.
- Pneumothorax – It is a condition in which air is filled in the pleural cavity.
- Cardiomegaly – Heart size enlargement
- Hemoptysis – bleeding in cough
- Pleural effusion- It is a condition in which fluid is filled in the pleural cavity.
- Tuberculosis it is a bacterial disease
Contraindication of this x-ray is
- Pregnancy because radiation will harm the fetus.
Patient Preparation
- remove some or all of his/her clothes and wear a hospital gown
- Asked to remove all of the jewelry, removable dental appliances, eyeglasses, and any metal objects or clothing that might interfere with the x-ray images.
- In female patients check LMP to follow the 10-day rule.
- Explain the whole procedure to the patient and ask them to feel comfortable.
Patient Positioning
- The patient is in an erect position facing upright bucky.
- MSP(mid sagittal plane ) is perpendicular to the IR(image receptor).
- Chin is raised above the IR.
- Shoulders are rotated anteriorly to allow the scapulae to move laterally off the lung fields and this can be achieved by either:
- Hands placed on the posterior aspect of the hips, elbows partially flexed rolling anterior
or
- Hands are placed around the image receptor in a hugging motion with a focus on the lateral movement of the scapulae
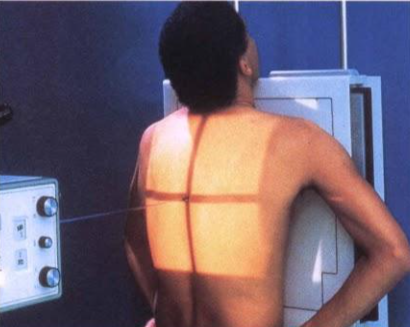
Central Ray
- The centering point at the level of the 7th thoracic vertebra, is approximately the inferior angle of the scapulae.
Image Evaluation
- The entire lung fields should be visible from the apices down to the lateral costophrenic angles.
- The chin should not be superimposing any structures.
- Arms are not superimposed over the lateral chest wall.
- Minimal to no superimposition of the scapulae borders on the lung fields.
- A maximum of ten posterior ribs are visualized above the diaphragm.